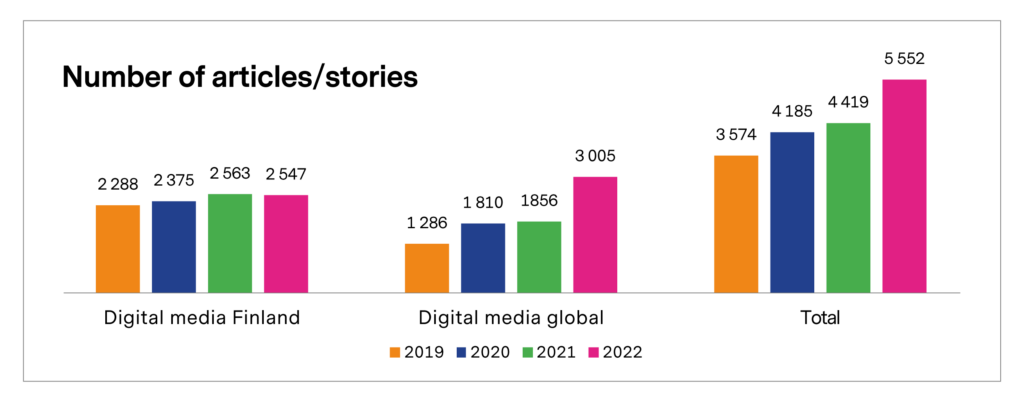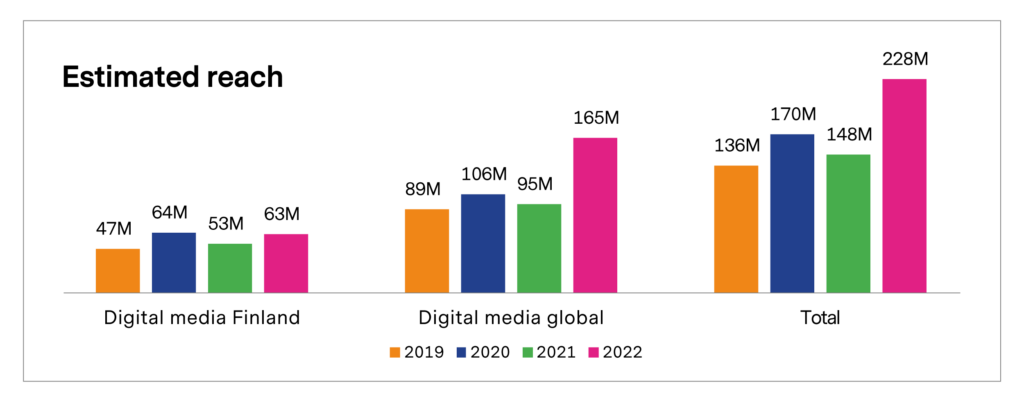HEI's self-assessment
Open and responsible science
Open and responsible science is promoted as an integral part of all research activities. Responsible science in the UO covers and combines the perspectives of good scientific practice, research integrity, sustainable development, diversity, responsible science communication and open science. The UO’s Declaration and policies of open and responsible science are presented on the website for responsible research. According to the UO policies, research outputs of publicly funded and published research are open and available for joint use, while the UO research infrastructures promote openness and sharing of resources. The UO has signed the Agreement on Reforming Research Assessment and joined the CoARA coalition.
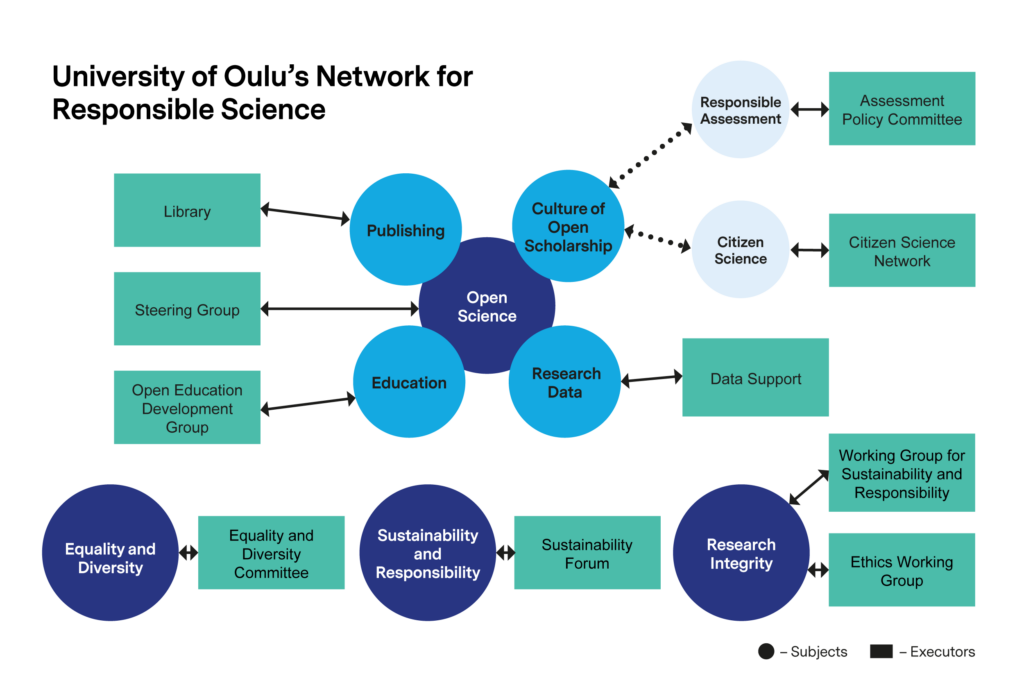
Figure 7. The UO’s Network for Responsible Science.
The UO’s open and responsible science policies, practices, services and network (Fig. 7) are coordinated by a steering group led by the Vice Rector of Research. The UO offers support for open access publishing, research data management, open education, responsible assessment, and use of publication metrics. Multidisciplinary Data steward team provides support for data management and engages in national and international cooperation. In 2022 the UO was ranked at the highest level in all sub-areas of the national open science monitoring model. This highlights the fact that the university’s policies, guidelines, and foresight work have been highly successful. In the follow-up of 2024, the role of support services will be greater and there is a risk that the current resources are not enough to keep the UO at a top level.
The UO has an active citizen science network to promote citizen participation and societal engagement. The UO will host the ECSA 2026 conference (European Citizen Science Association) and has established the Finnish Citizen Science Association. The UO is one of the ten European University UNIC partner universities which promote community engagement and the popularisation of science.
The UO’s Research Council supports the rectorate in promoting research, assesses the quality of research activities and is also partly responsible for guiding the quality work of research. The UO has committed to follow the guidelines of the Finnish National Board on Research Integrity (TENK) and the European Code of Conduct for Research Integrity. Researchers’ commitment to the principles of research integrity and ethics is part of the UO’s quality assurance. The UO personnel and students are familiarised with the responsible conduct of research guidelines via extensive education.

Figure 8. Key research results, 2021.
The societal impact of research
The OU’s multidisciplinary scientific community is generating impressive research results (Fig. 8) on tackling global challenges. Multidisciplinarity is purposefully advanced in the UO’s strategic decisions of profile areas and by focus institutes to increase the quality of research and societal impact. Thematic ensembles are coordinated by the focus institutes that support networking between disciplines and faculties, interdisciplinary projects, and doctoral education. The Thule Institute coordinates Arctic activities, including cooperation with the Arctic University Network.
The actual and future impact of the research is assessed regularly by an international panel in the RAE process. One of the key findings in RAE2021 was that all research units are aware of the importance of societal impact, and they have special efforts directed towards regional benefits. An example of impactful research is the recent nomination of Prof. Heli Jantunen as one of the Academicians of Science.
The UO has a unique scientific profile linked to the UN’s global Sustainable Development Goals. The UO is committed to acting responsibly towards society and environment, to seek solutions to the sustainable use of resources, and to make ecologically responsible choices in its own operations. The Sustainable Development Working Group has prepared an Action Plan on Sustainability and Responsibility. The UO is actively influencing regulation at different forums sending statements to ministries and national agencies, EC offices and UN organisations.
Research and project services offer impact workshops and an online Impact Helper guide with a concrete Impact Planner tool. Special emphasis is placed on support for young coordinators of Horizon Europe pillar II proposals, especially for the impact section. This has led to excellent results and the number of coordinated HE consortium projects has risen from 9% in H2020 to 18% in HE.
The UO has a vital role in the R&D activities of the Oulu region. The UO supports the ICT sector of the area through its globally strong 6G research. Additionally, the metal and forest industries as well as the health and wellbeing sectors are scientifically supported through constant productive interaction with the sectors.
The UO co-leads together with University College Cork, and Malmö University UNIC Centre for City Futures, that integrates education and research, and service to society. It is a One-Stop-Shop infrastructure for systemic cooperation with 10 UNIC cities, to develop collective regional capacity and capabilities beyond boundaries, by enabling 10 UNIC universities engage with cities, communities, and stakeholders for transformative innovation and societal impact. The UO as part of the European University UNIC is committed to the European Declaration on Engaged Research. According to its definition, Engaged Research is an overarching term that describes a wide range of comprehensive research approaches and methodologies that share a common interest in collaborative engagement with and within society.
The societal impact of innovation activities
Besides coordinating company collaboration the UIC is an internal service unit for researchers in inventions, patenting, and research-based business development. The UIC manages the university patents and technologies, and other IP portfolio, and negotiates all the technology and material transfer agreements. UIC also helps faculties and research units to make NDAs and collaboration agreements with customer organisations.
The UIC has internal instructions concerning inventions and patenting before publishing if the invention has the potential for commercialisation. The UIC also provides business development support for researchers with research-based business ideas and plans for startup companies. The procedures for technology and IP transfer to companies are in place and transparent. The innovation activities and results are monitored (Fig. 9) and the UIC activities are tuned if needed.
Place-based innovation ecosystems’ capacities are increased through radically expanded mobility and diversity of participants by UNIC CityLabs.
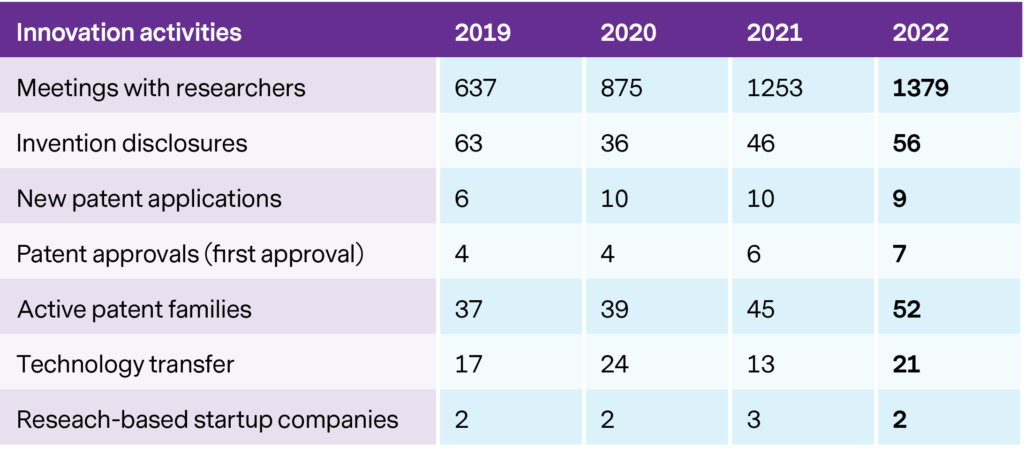
Figure 9. Innovation activities.
Communicating scientific activities and the impact of the university
The public, sponsors, influencers, and various professional groups are interested in knowledge, as well as novel scientific research and partnership opportunities provided by the university. Through media outlets, the university can reach out to large audiences, participate in social debate, influence, and raise the profile of the UO’s scientific community. Communications specialists at each faculty help the media to find information and experts. Some service units also have their own communication activities and channels for stakeholders. The university has several regular newsletters for external recipients. The university’s monthly newsletter focuses on science and research, and the recipients include alumni, partners, and other stakeholders.
The UO has official social media accounts on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, Snapchat and TikTok managed by the Communications unit. The channels highlight the university’s results and impact. The UO encourages employees to participate in societal discussions according to their role as scientists or teachers. Social media is used by the university for marketing and communications, recruitment, teaching and interacting with stakeholders. UO Communications constantly follow and analyse the media presence of the UO and the UO’s research in the national and international media, including social media.
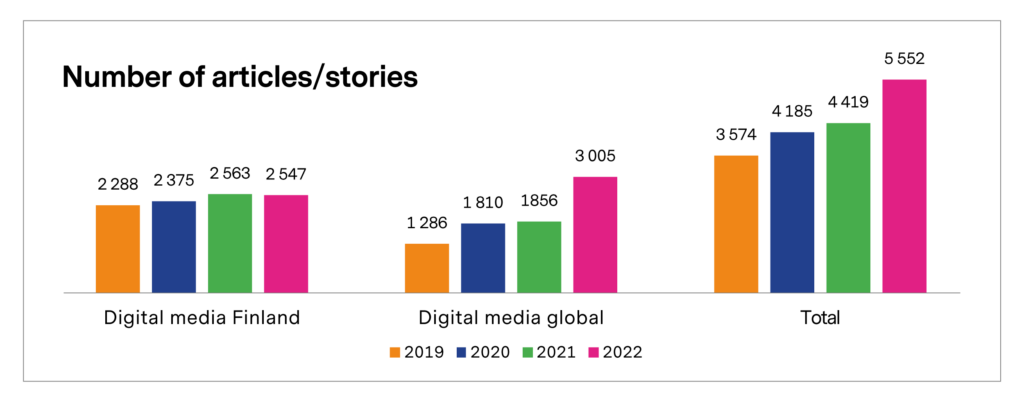
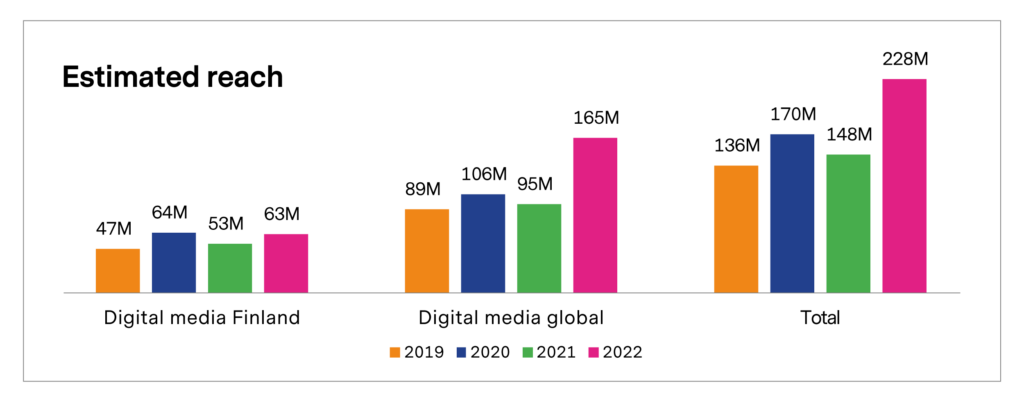
Figure 10. Digital media coverage 2019–2022
| Strengths |
Enhancement areas
|
| Citizen science. |
External website for collaboration needs content. |
| Multidisciplinarity within research focus areas. |
Future resources for support of open and responsible science. |
| UIC to coordinate company collaboration and innovation activities. |
Societal engagement in terms of international employees. |
UO’s multidisciplinary research reforms society
The University of Oulu takes part in multidisciplinary research and many research networks. The project portfolio covers a variety of topics in sustainability and climate, biodiversity, technology, society, and human subjects. The cross-networking and interaction as well as multidisciplinary research work is a unique advantage for the UO in terms of creating new innovations and contributing to transformation in the society. The existing multidisciplinary focus institutes support the strategic development of research activities.
At the University of Oulu, multidisciplinary research is conducted in five focus areas. The basis for multidisciplinary research is created by long-term basic research. Research is structured as a matrix organisation. In addition to faculties, disciplines and research groups, there are focus areas and focus groups for cross-faculty interdisciplinary research. In addition, the university has strategic programmes and strategic funding. According to the audit visit, researchers were appreciative of the structure.
Long-term view of research impact could be emphasised
The university has linked its scientific profile to the UN SDGs. The targets of research impact at the university are to act responsibly towards society and environment, to seek solutions for the sustainable use of resources, and to make ecologically responsible choices in its own operations. There are excellent metrics such as the number of start-ups created through the joint projects. According to the audit visit, research impact is also measured by the number of patents, research and innovation projects, and meetings with partners. The metrics are mainly quantitative. The university also obtains important information on research impact from the Research Assessment Exercise (RAE), last carried out in 2019-2020. According to the RAE2020, there is a strong link between the scientific activities of the UO research units and the SDGs.
The audit team notes that the university could benefit from additional long-term metrics for research impact. For example, following the number of new start-ups is important, but the university could also benefit from following the impact of such start-ups in the long term. This information could be critical in terms of deciding future initiatives. Long-term metrics are particularly useful and necessary for enhancing future-oriented research activities. The university could also gain useful information by adding qualitative measures of research impact in areas that are not easily measured by quantitative measures. Examples include an increase in awareness, well-being, or policy changes that are influenced by or based on research findings.
According to the audit visit, the UO researchers’ aim is to reform society. Reform starts with defining existing reform needs in the society. After that, researchers can start the research. To help researchers, the university has developed the Impact helper guide. It covers the concept of research impact, impact pathways, possible stakeholders, and ways to maximise and measure impact. The guide assists researchers in finding links between their research and the UN SDGs. In addition, the university offers customised research impact workshops which are organised for research groups. The audit team recognises the Impact Helper as an excellent initiative to support and engage researchers to evaluate and consider the impact of their research from a global perspective.
The University of Oulu’s Arctic Strategy is an important opening for joint research
During the audit visit, the audit team was impressed by the Arctic strategy of the University of Oulu. The strategy focuses on addressing the challenges and opportunities in the changing Arctic region, driven by factors such as climate change, globalisation, and demographic shifts. The strategy aims to integrate Arctic research into the university’s overall objectives. The audit team finds the university’s emphasis on building a sustainable Arctic through collaboration with various stakeholders and multidisciplinary research commendable.
The university’s Arctic strategy highlights key topics including resilience, One Health, and sustainable governance of natural resources and business in the Arctic. At the core of Arctic research, the university emphasises the creation of new knowledge, taking responsibility, and succeeding together through inclusive and diverse networks. Arctic research has been selected as a key strategic area and a strong basis for the future.
Strengthening the visibility of international research and cooperation
Focusing the university’s profile strategically is necessary to help it reach its goals of world class research and collaboration. The audit team suggests strengthening the visibility of the university’s strong collaborations with international organisations such as the Arctic Network and the European University of Cities in Post-Industrial Transition network (UNIC). Through active communication, the university could draw attention to the concrete effects and advantages of these partnerships for researchers, students, faculty members, and the public. The university’s communication unit and communication specialists at each faculty play a key role in this. Their role should be highlighted among the research staff.
The audit team notes the importance of communicating research results at both local, national, and international levels. According to the audit visit, research communication has been invested in for many years at the UO. There are several common practices at the university which support communication and interaction related to research, like involving external stakeholders in research programme meetings, events, and different working groups.
The university enhances open science
The audit team found evidence that open and responsible science characterises the policies, practices, services, and networks at the University of Oulu. The UO is committed to open science as a signatory of the national Agreement on Reforming Research Assessment. The UO has also joined the International Agreement on Reforming Research Assessment (CoARA) and signed the International Dora Declaration. In addition, the university has its own Declaration and policies of open and responsible science. Researchers and doctoral researchers are encouraged to publish in open access journals with the highest possible JUFO classification. The university library and network of open science play a major role in promoting and supporting open science at the university. The university has also an active citizen science network to promote citizen participation and societal engagement.
The University of Oulu is committed to the Finnish code of conduct for research integrity and procedures for handling alleged violations of research integrity in Finland 2023 guidelines. The UO is also committed to the European code of conduct for research integrity. The university has an ethics working group, and its tasks include discussions about the university’s values and ethical questions. Ethical review of medical research in advance is a statutory process managed by the regional medical research ethics committee of the Wellbeing services county of North Ostrobothnia. In addition, the ethics committee of human sciences at the UO gives statements on non-medical research projects of human sciences and process related ethical issues.
The University of Oulu provides general training in responsible conduct of research. Otherwise, research ethics are considered in daily research and monitoring. Supervisors play a big role as role models for conducting ethical research. Research ethics training is compulsory for all doctoral researchers and later for all new researchers. The researchers described research ethics as being integrated in ordinary research.