Pedagogical vision guides planning
Our pedagogical vision is founded on dynamic competence, connecting learning with work life and offering flexible and diverse learning paths. Students are active agents, and our teachers work together, sharing knowledge and creating new information and methods.
Curricula linked to strategy
Our education has undergone a major reform derived from our strategy. The process started with master’s level in 2019, followed by bachelor’s level and continuous education in 2022. The staff, students, and stakeholders all participated in the curricula renewal.
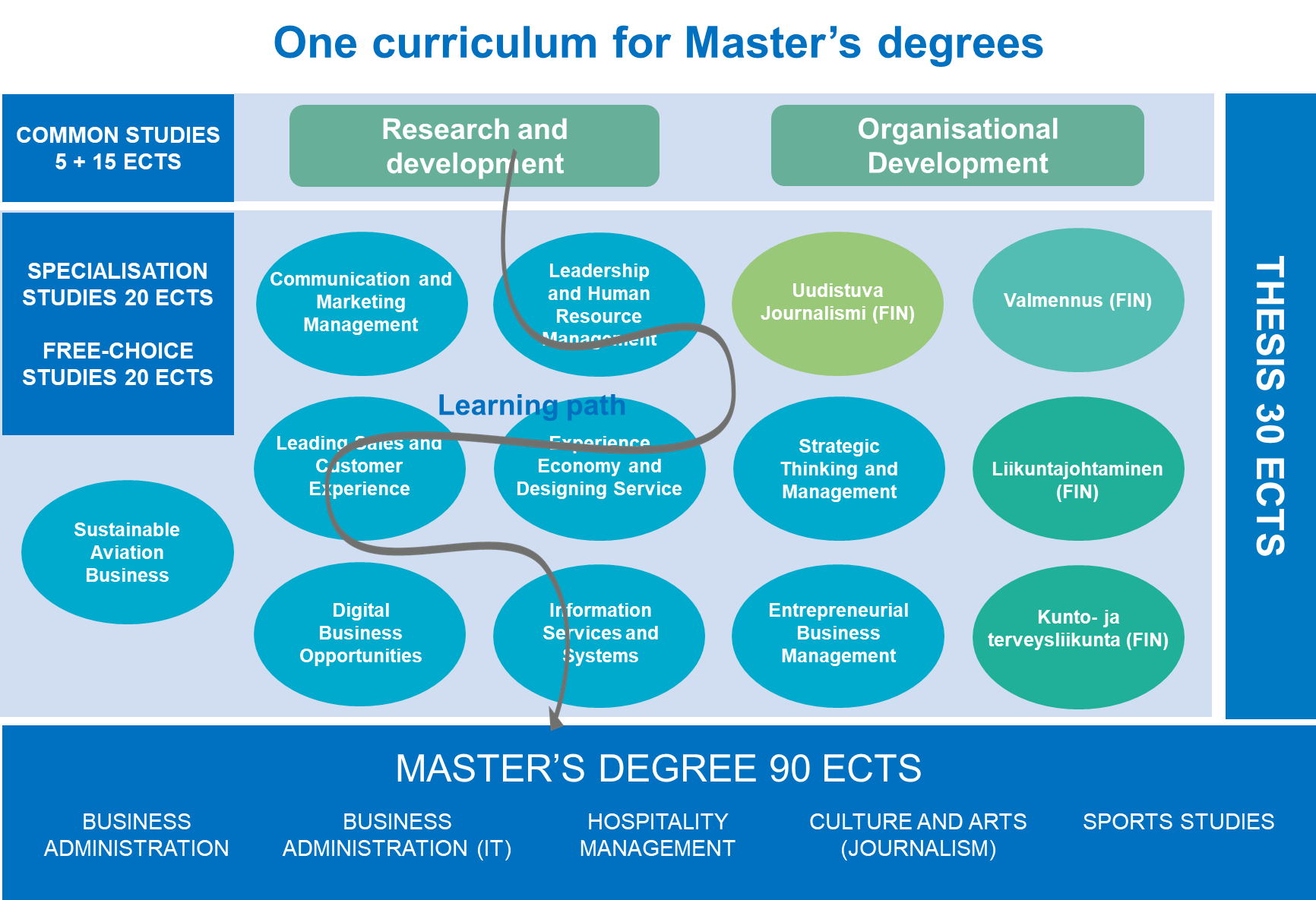
Picture 7. One curriculum for Master’s degree
In the new curricula, specialisations complement each other, creating more diverse study options. We noticed that the variety of options requires more guidance, and a new student counselling model was created. It is currently used for bachelor’s level and being adopted to the master’s level as well.
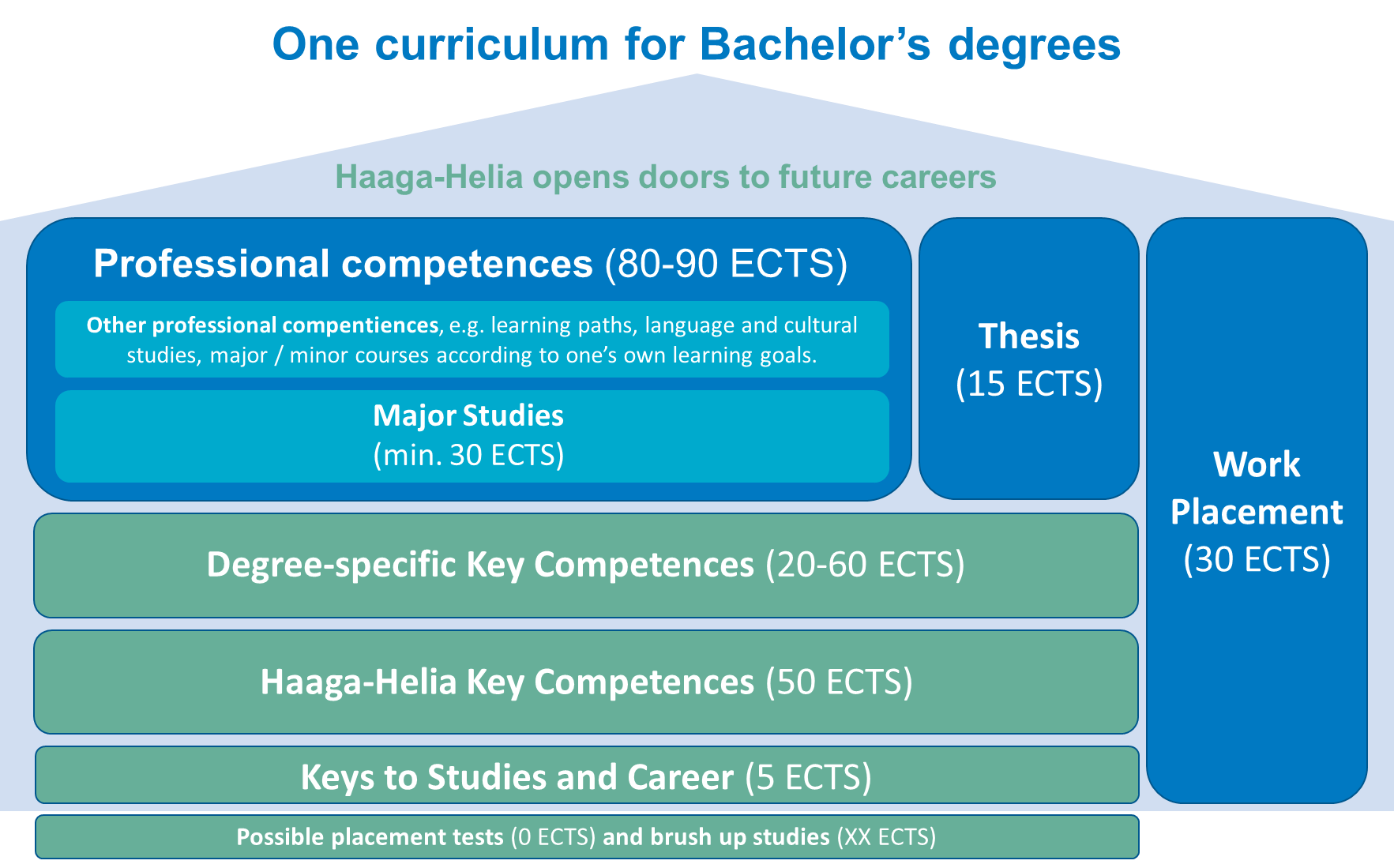
Picture 8. One curriculum for Bachelor’s degree
Our curricula structure allows flexible tuning and updating. Changes to the degree requirements that affect the curricula structure are taken to the Management Group and the Collegiate Body for approval. For each strategy year, certain focus areas are selected. To ensure that the strategic goals are turned into operational activity, they are discussed at the new OSTU (Osaamisen tulevaisuus-Future of Competences) forum. At the monthly OSTU meetings, the supervisors of the educational areas meet with Management Group and the competence area and research area directors. The agenda is often heavy, and focus needs to be on the strategically important issues.
Opening doors to international careers
The contents and learning objectives of our curricula are based on a strong theoretical background and constantly reviewed to meet the needs of various industries. We have an active partner company network enhanced by teachers’ own contacts and collaborations. The relevance of education to businesses is ensured through continuous dialogue, also taking place during course projects. Through company cooperation, work placements and projects students create networks. Education reform has strengthened collaboration and unified practices.
Our curricula are planned to ensure international competences, and to enable a study period abroad. We offer language and culture studies, as well as many other courses taught in English with multicultural study groups. Students are encouraged to complete an exchange or a work placement abroad. The mobility period is included in the individual study plan and credits completed abroad recognised as part of the degree. International Services give support, guidance and funding for mobility. The pandemic has decreased mobility and we need to work on reaching future targets.
Flexibility supports continuous learning
Continuous learning is organised through the Open University of Applied Sciences (Open UAS). The course selection at the Open UAS is based on the courses in the degree curricula. Our new modular curricula structures support continuous learning and the needs of our Open UAS students through flexibility. The Open UAS course portfolio is constantly reviewed and renewed based on the demand from learners and employers.
The education reform has brought variety to our course implementation methods, which are contact, blended, online and virtual. Our day-time programmes offer more contact implementations, whereas in multiform programmes online and virtual implementations are more common. While the reform brought flexibility to the methods, the descriptions and assessment criteria were unified. Each course has assessment criteria for grades 1, 3 and 5. Teachers are provided with templates and workshops to help to formulate the course descriptions supporting equal assessment.
Planning based on European structures
Our degree qualifications are built on the European EQF levels. The intended learning outcomes of our programmes are based on the European EQF levels 6 and 7, corresponding FiNQF levels 6 and 7. The planning is based on current research and the needs of our stakeholders, including the staff, students, alumni, as well as our national and international partner companies and organisations. In planning the workload, we follow the ECTS (European Credit Transfer System). In competence-based education, the workload varies from student to student. Our teachers are well trained, and we trust their expertise in the evaluation process.
Student feedback contributes to the planning. Estimating the workload is part of feedback and students are encouraged to reflect on the intended learning outcomes. Students, alumni and businesses are invited to the education planning workshops. As the planning process is practice-oriented, we have noticed that the theoretical basis needs to be documented more clearly.
Curriculum changes are taken to the Management Group and to the Collegiate Body. Degree level development is discussed in degrees and with relevant competence areas, as well as in OSTU meetings. Due to many discussions, the procedure might be time-consuming.
Projects contribute to education planning
Our lecturers and principal lecturers are active in RDI projects and integrate project work in their courses. Projects also ideate thesis topics. Research is also linked to education through involving lecturers and students in projects. All staff members are encouraged to participate in project applications and in funded projects, also benefiting education planning. New projects search for members through eg., our intranet’s Competence Market. The procedure works quite well but depends on the activity of individuals.
| Strengths | Enhancement areas |
| Education reform enables a wider choice of studies for the students | Education reform challenges the planning of course portfolio |
| Working-life relevant education and agile reactions to changing environment | Counselling for ensuring relevant course choices |
| Applying advanced and modern learning environments | Systematisation of collaboration with companies and other stakeholders |