Quality management and strategic management form an entity
Metropolia’s quality policy is public, and the objectives and responsibilities of the quality system are described in section 5 of Metropolia’s rule of procedure. The purpose of the quality system is to support the achievement of strategic and operative goals (figure 13). The responsibilities of quality management have been divided in accordance with the management system responsibilities. Management group members have a direct responsibility for the five themes of Metropolia’s strategy. The different roles have been described and a responsibility matrix has been created to clarify the responsibilities and division of work between different positions and roles.
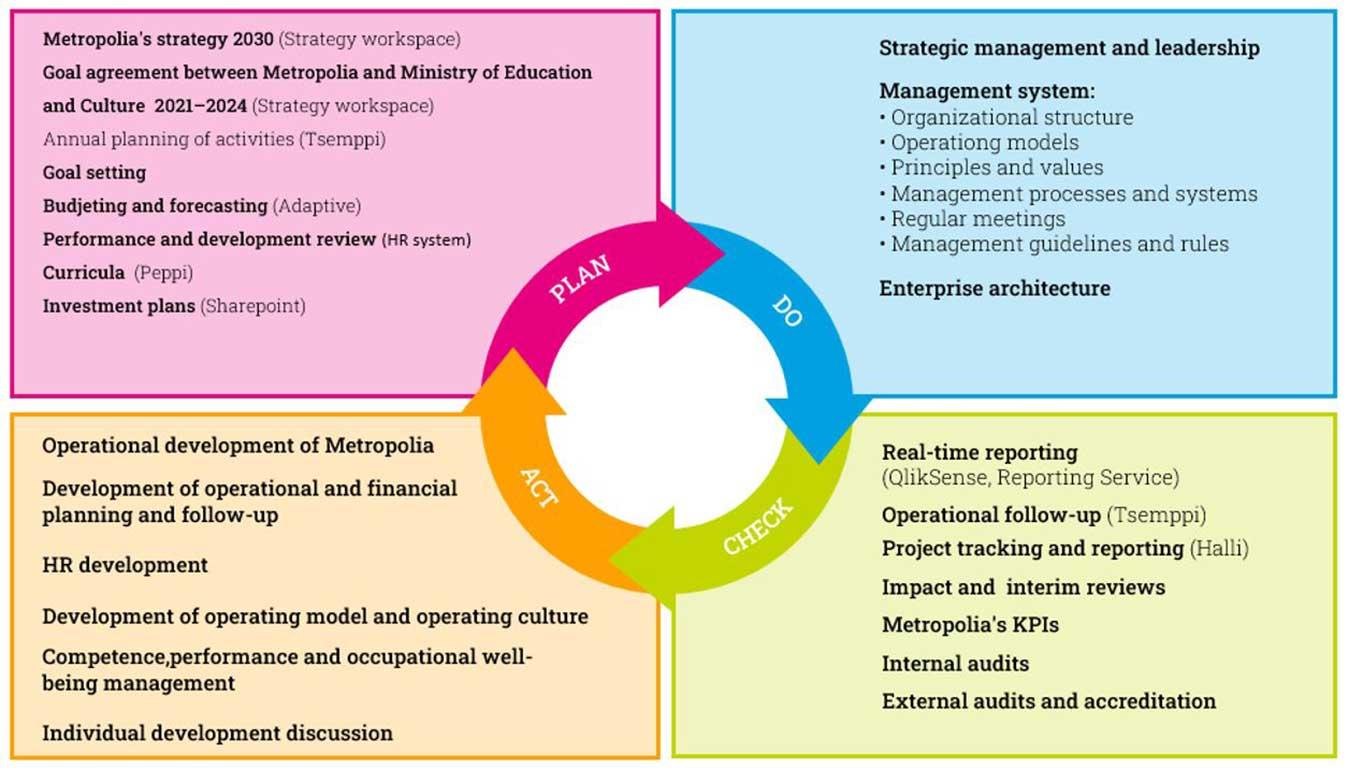
Figure 13 Management and the quality system form an entity.
Strategy 2030 defines the organization’s strategic intent, strategic themes, and their key objectives for the strategy period. The strategy takes into consideration that different functions and units are at different stages of their life cycles with regard to the strategy and gives the units flexibility in the planning of their next steps.
To promote the various themes in strategy, documents have been created that help deploy the strategy in practice, such as the road map for sustainable development and the RDIL road map. They help the units and people responsible conceptualize the measures that Metropolia needs to take to meet the objectives set in the strategy. These road maps, like the strategy, have also been prepared by means of participatory methods.
Strategy dialogue provides more insight into the strategy throughout the strategy period and in accordance with the management system. During strategy days, the management group and middle management, as well as personnel and student representatives, discuss the themes. The discussion continues in leadership forums. In KampusAkatemia events, the management and entire personnel discuss the themes of the strategy. The management briefings are used to communicate topical strategy-related matters and the development of indicators impacting performance bonuses. The strategy is also the starting point in the individual performance and development discussions conducted annually. The preparations for the discussion include the familiarization with strategy, action plan and the measures of the unit in question as well as an examination of one’s own work in its context.
Practical quality management visible in operations management
Annual operations management incorporates strategy in the organization’s daily activities (figure 14). Metropolia’s operations and finance are planned and monitored in accordance with a shared annual planning cycle.
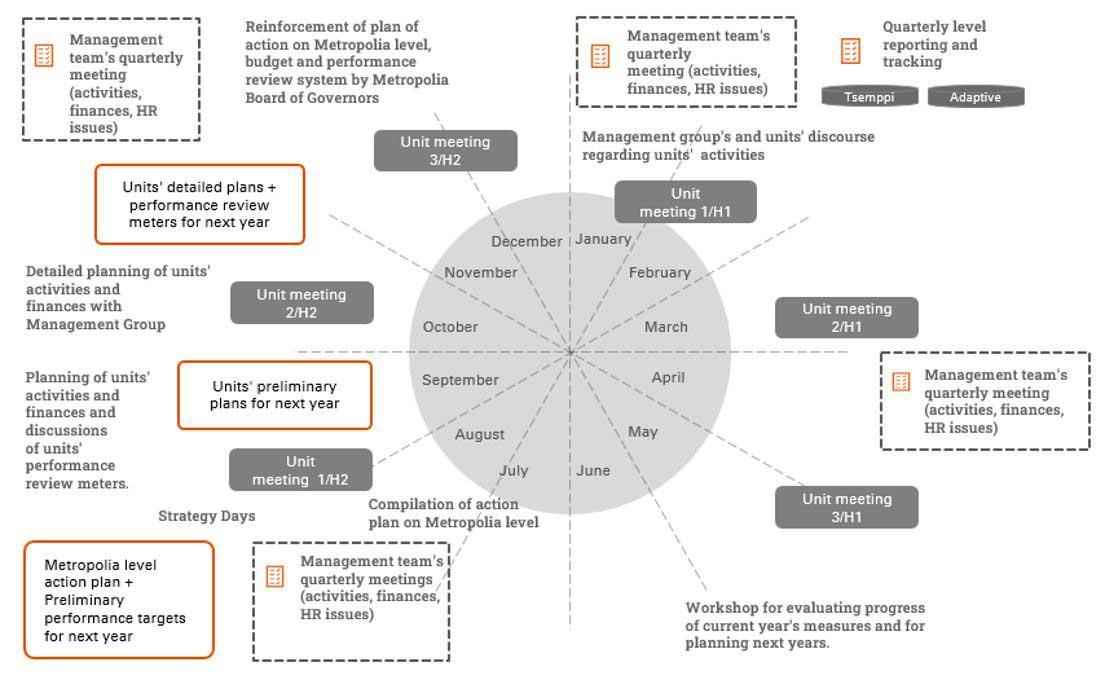
Figure 14 The annual planning cycle of the planning and follow-up of the operations and finance
The planning cycle of the operations and finance is launched late in the spring with assessing measures entered in the current year’s action plan and progress of objectives. Guided by this assessment, the changes identified in the business environment and the strategy, the management group summarizes Metropolia’s action plan for the following year and selects shared performance targets. The allocation of resources for the most important targets of the action plan are agreed in a centralized manner. The management group and middle management review the action plan and the shared objectives included in it during the strategy days held at the beginning of the fall semester. In addition, the event includes building a shared understanding of the strategy, its progress, and the action plan for the following year, as well as supporting the persons responsible in each unit in linking this entity to the planning of the operations and finance of their respective units. The units themselves select some of the performance targets.
Annual action plan and the units’ measures are entered in the Tsemppi planning and follow-up system where they are accessible to the entire personnel. The persons responsible for the measures report on the progress at the end of each quarter. The management group regularly monitors the progress of Metropolia’s action plan and targeted indicators. The information entered in Tsemppi is used in compiling impact reviews, published quarterly. Unit-specific progress is monitored by the units’ management teams. The role of the unit management teams has been strengthened in operations management to support middle management and to develop cooperation, competence, and management.
Structures and procedures support management
Management and the achievement of the strategy targets is supported by means of appropriate tools and information systems. The enterprise architecture and operations management link the annual management processes to each other in terms of time and content. The development work completed on processes, schedules and information systems has made the planning round in the autumn smoother.
One of the main objectives of knowledge and data management has been to provide up-to-date and appropriate information to management for decision-making. For example, the Qlik Sense data visualization tool allows for monitoring the development of key indicators both on the level of Metropolia and each unit. Qlik Sense is currently being developed to support horizontal supervision of the core operations and the access to information by the unit management teams.
Metropolia’s enterprise architecture offers a systematic approach to outlining the organization’s operations and structures and to developing and administering them in a comprehensive manner. The enterprise architecture is connected to the processes of operations management and development. Applying enterprise architecture helps to ensure the compatibility of operations and information and to avoid overlapping solutions (such as ICT systems). More detailed information on the development of the architecture is provided in chapter 3.4.
Project management is supported by means of a shared project model which defines the roles and responsibilities of project management and the decision-making process to complete the project. Following the project model ensures that the development projects and RDI projects to be implemented are appropriate and smooth. Challenges experienced in the implementation of the project model include the level of competence in project management, the frequency of data entry and the quality of data. Since June 2022, a prerequisite of working as a project manager in RDI projects is the completion of the project manager training.
| Strengths |
Enhancement areas |
| Metropolia’s quality system supports the realization of Metropolia’s strategic and operative goals. The management responsibilities related to the strategic themes have been described in the management system and divided in accordance with the quality system. |
A more systematic collection and application of forecast information is important strategically and from the perspective of all core operations, and a related development project is under way. |
| There are participatory opportunities for the entire personnel and students to engage in dialogue and have an impact in the strategy creation and implementation stages. |
Strengthening systematic operations management and knowledge management in management team meetings on the unit level. The practice is new and needs to be instilled in the operations. |
| The enterprise architecture has been used actively in the development of operations, and the architecture is linked to and supports operations management and strategy implementation. |
Applying the project model and project management. In addition to training, project managers need more practical support. |

