Education planning guided by strategy
Education planning at Metropolia is guided by the strategic theme of Lifelong learning, which covers all degree programmes and other learning solutions (figure 3). Education planning is also guided by pedagogical principles and other strategic themes.
Phenomenon-based learning takes place in innovation hubs. Sustainable development and growth guides Metropolia to incorporate the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals in all education. The People and culture theme supports the Metropolia community on its journey towards an agile learning culture and bold experimentation. Digitalization guides the use of digital tools in the development of learning. In education planning, a need for more systematic development has been identified. The degree programmes will draw up development plans by the end of 2022 for the implementation of the pedagogical principles and strategic themes. In addition, the steering group of the Open UAS began operating in the beginning of 2022. HEI-level coordination of preparatory education for specialization students and immigrant students will be launched at the group’s initiative in the autumn of 2022.

Figure 3 At Metropolia, all learning is lifelong learning.
The education planning at Metropolia has been consistently taken in a more learner-centric direction (see 1.4). The concept of lifelong learning covers all education ranging from studying for a degree to other learning solutions. Learning is based on the Metropolia Match® model (figure 4) which brings together an individual’s competence needs, societal needs and professional life, as well as flexible learning solutions and guidance services based on demand (see 1.4). The goal is to smooth out transitions between educational levels, maintain and renew competence, support career changes, strengthen entrepreneurship, promote employment, and strengthen inclusion.
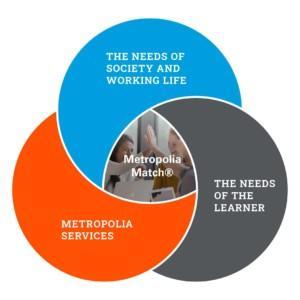
Figure 4 The Metropolia Match® model
Curriculum work ensures the quality of education
Metropolia has an established process of curriculum work in place. In accordance with the degree regulations, the curriculum defines the learning outcomes, contents, prior knowledge requirements and evaluation criteria as well as the scheduling and scope of the studies. The curriculum work is guided by strategy, pedagogical principles, relevance to professional life, internationalization goals, as well as the alignment with the international degree framework and education-related norms and regulations. Various types of feedback from students is applied in the curriculum work. Development trials on using artificial intelligence have been carried out in the curriculum work (see 1.4). The trials include the assessment of professional relevance for the curricula, learning contents of sustainable development and the recommendation of studies that supplement the learner’s competence. Using artificial intelligence in curriculum work will be processed further in a project that develops predictive capabilities.
Metropolia’s curricula are competence-based. The learning outcomes and the competence to be accumulated during the student’s study path have been defined. This supports the student-centric education, the recognition of prior learning (RPL), the preparation of evaluation criteria and planning of course implementations. In accordance with the Metropolia Match® model, curriculum work also takes into consideration the needs of non-degree-awarding education for different customer groups, e.g. the offering of the open UAS, specialization studies and preparatory studies for immigrants.
The curricula are updated annually. The extensive curriculum reforms are scheduled in line with strategy periods. The curriculum work in the degree programmes is the responsibility of the heads of schools, who are supported by the management teams of their respective schools. The director of Lifelong Learning approves the curricula and the extensive study modules. The head of school approves the field-specific study modules. The smooth progress of curriculum work is supported by the Learning Development Unit through instructions, support measures and personnel training. The Learning Networks and Services unit as well as the Student and Admission Services direct the planning of solutions in non-degree-awarding education.

Figure 5 Process for establishing new degrees
The process for establishing new degree programmes has been renewed and will be implemented in the autumn of 2022 (figure 5). Development needs have been identified in the study place process. Process renewal is under way. The management group discusses the proposals for new degree programmes/educational provisions and study places and submits a proposal for the Board of Directors to consider. The Board of Directors makes the decisions regarding the number of study places and the new Master’s degree programmes. The change proposals related to educational provisions (Bachelor’s degrees) are submitted to the Ministry of Education and Culture.
In education planning, the opinions of Metropolia’s stakeholders are mainly received through advisory boards. The majority of schools and some of the degrees have their own respective advisory boards that process the curricula. The majority of the advisory board comes from the business world while the rest of the members are personnel and students. The advisory boards have a long history. As a consequence, there is some inflexibility and need for renewal, such as increasing the participation of students in education planning.
Planned learning support
The implementation and evaluation plan for individual courses is based on the course descriptions in the curricula. The planning covers practical solutions concerning teaching and learning, learning environments, study materials, work format and workload, teaching methods, alternative completion methods and principles and methods of evaluation. The study workload is measured with ECTS credits. A collective form has been created to support workload planning and to ensure consistent quality. Pedagogic staff members consisting of experts and teachers experiment with and promote good practices in a collegial manner.
The RDI activities and artistic activities have been integrated into teaching in various ways. All degree programmes include an Innovation project. The students are offered work placement and studification opportunities through the innovation hubs’ collaboration platforms and RDI projects, and the Turbiini Campus Incubator offers entrepreneurship studies.
The two-phase operating model formed by the curriculum and the implementation and evaluation plan is quite flexible. It allows the teacher and the team of teachers to make changes and adjust the operations based on the students’ needs. The operating model gives the teacher the freedom to plan the implementation and evaluation in the best possible way in any special circumstances as well. This became quite important in navigating the change requirements caused by the Covid-19 pandemic in the spring of 2020.
| Strengths | Enhancement areas |
| Defining lifelong learning to include all learners and their learning paths in full. | The planning process for the provision of non-degree-awarding education should be simplified. |
| The process for curriculum work in degree-awarding education is transparent and adopted across the board. | A systematic approach on the HEI level in the planning of degree programmes and a strong link to the strategy; completed development plans for degree programmes by the end of 2022. More extensive utilization of artificial intelligence in the development of education. |
| A flexible, two-stage operating model for the planning of education specific to each degree programme. | Renewal of advisory board functions; involving the business world in the education planning. Students’ opportunities to participate in the planning should be increased. |
| The activities of the pedagogic staff members incorporate the view of teachers and experts in the pedagogic planning and collegial activities. |