Högskolans självvärdering
RDI and artistic activities renew the society
The innovation hubs produce projects, education implementations, MINNO studies and services on the campuses’ collaboration platforms. Special focus is placed on entrepreneurship services and the deployment of innovations in practice as part of the Helsinki Metropolitan Area’s Campus Incubators programme and the 3UAS Entrepreneurship Society. The operations of Turbiini have expanded to all campuses, and access to Turbiini has also been granted to actors outside the HEI community. Metropolia’s artistic activities are intricately linked to the RDIL activities and the innovation hubs’ themes. Close ties to education are manifested in opera education, for example, in which multidisciplinary RDIL activities enable opera productions.
Metropolia applies its extensive cultural sector and offers the know-how of the creative fields for use in other fields, which strengthens the societal impact of the creative fields. One of the first significant cooperation outcomes is the Creativity and Arts in Social and Health Fields – Master’s degree, which renews the utilization of creativity, culture and art in health care and social services. Another example is the Mahdollisuuksien maisemia (Landscapes of Possibilities) event, which promotes taking the opportunities provided by creativity into consideration in various sectors and occupations of the business world. Metropolia has also integrated its expertise in creative fields and technology with the development of urban environments, and became the first Finnish UAS to be selected as a partner in the New European Bauhaus initiative (see 2.4.).
The management of the RDI activities and innovation hubs has been developed to meet the needs of systemic management and working in an ecosystem. Innovation Directors are responsible for the operations and development of the innovation hubs. The RDI Services unit supports the project activities, the funding applications, and the publishing activities. The Innovation and Entrepreneurship unit supports the operations of the innovation hubs and schools in the innovation ecosystems by developing the collaboration platforms and student-oriented entrepreneurial activities. The coordinators for the innovation hubs’ thematic areas have been assigned themes that transform the contents of each innovation hub into a concrete form (Figure 11). They strengthen cooperation between the educational content and the innovation hubs.
Quality management supports the RDI activities
The planning of innovation hub activities is based on annual implementation plans and on school-specific RDI plans in Education (figure 12). Changes in the operating environment are monitored through continuous dialogue with various actors in society. Information is gathered from the user/experience interface for the needs of new learning environments, education, and projects. In addition, international RDI and policy programmes and opinions are monitored and analyzed.
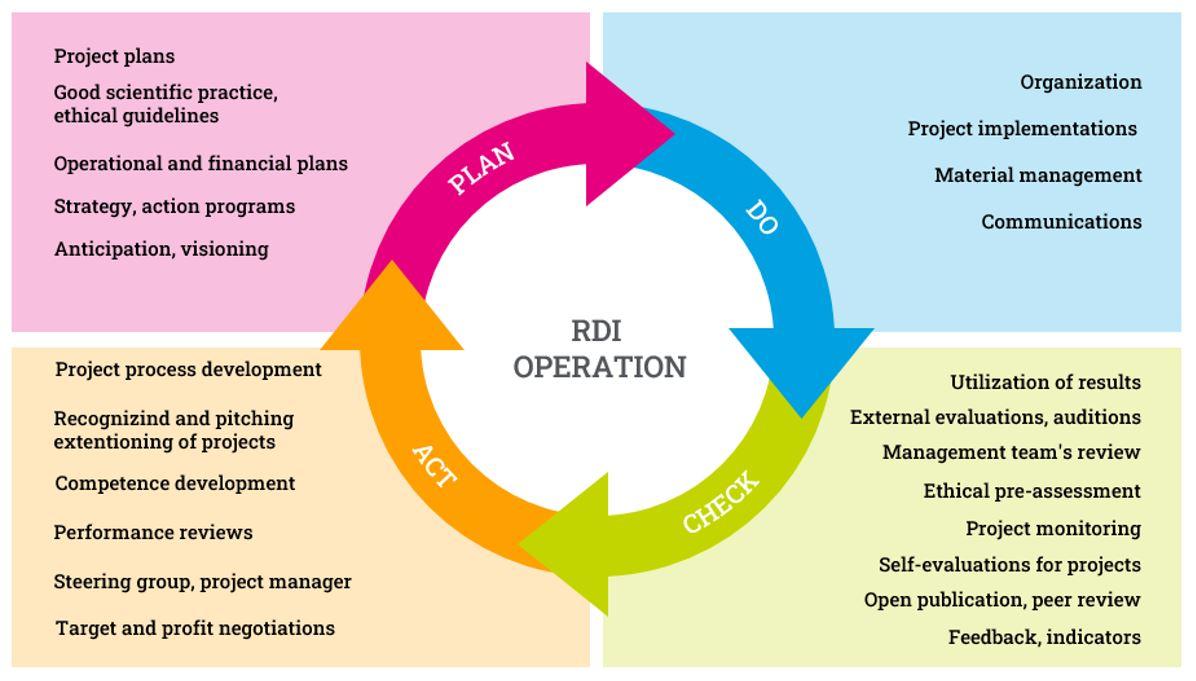
Figure 12 The management of the RDI activities and quality management are interlinked.
The implementation of the RDI activities has been described in the OMA intranet. The RDI projects and the project portfolio are managed in accordance with Metropolia’s project model. They are monitored in the Halli management system. A significant portion of Metropolia’s external funding is channeled via project operations. This is why using Halli supports Metropolia’s financial management. Project management at Metropolia (only in Finnish) consists of progress stages and decision-making points, roles and any related responsibilities, as well as project management documentation. Project management guidelines are available in the OMA intranet, as are the instructions for other RDI project operations. Strategic selections and policies concerning intellectual property rights have been approved by the Board of Directors and published as the IPR Strategy. The innovation hubs publish scientific and popular articles in, among others, publication series, specialist blogs and podcasts. The library is responsible for the collection and reporting of the publication data.
Metropolia communicates information about research, innovations, and artistic activities to its stakeholders in newsletters and through social media channels and the Metropolia website. In the self-assessment, strengthening the hubs’ communication was highlighted as an area of enhancement. It has since been addressed with new recruits for communications services.
The RDI activities are assessed by means of feedback surveys and feedback events aimed at customers and collaboration platform partners. Projects are assessed at decision-making points included in the project model, in steering groups and with self-evaluations. RDI activity services collect internal feedback. Information on progress is entered in the Tsemppi system. It supports assessing the impact of the innovation hubs. According to the self-assessment, verification, and assessment of the impact of RDI activities should be more strategically managed and more consistent and open. Feedback collection practices should also be strengthened which has been taken into consideration in planning operations for 2023.
Current development targets of the innovation hubs are related to the RDIL activities, student entrepreneurship and cooperation with businesses especially on the campuses’ collaboration platforms.
Metropolia is committed to promoting open science and responsible conduct of research
Nearly all of Metropolia’s publications are freely available in the Open Repository Theseus. They are published under the open Creative Commons license. The Metropolia Research Data Policy document includes the promises, guidelines and principles to be implemented related to Metropolia’s research data. Deploying good data management practices and open RDI activities in the operating culture is supported by means of data agents.
Metropolia is committed to complying with the guidelines of the Finnish National Board on Research Integrity on the responsible conduct of research and the processing of suspected violations thereof. Induction to responsible conduct of research and teaching research ethics are part of the studies. Every Metropolia RDI project manager peruses the RCR Guidelines and the principles and operating models of the open RDI activities as part of project manager training. Any suspected violations of the RCR by Metropolia’s actors are dealt with an agreed process. The quality and functionality of the process for suspected violations of the RCR have been developed as part of the records management plan and the case management system. Metropolia employs two research ethics support persons, providing easy-to-access guidance and training on research ethics to RDI actors and thesis instructors. Metropolia is an active participant in the Human Sciences Ethics Committee of the Helsinki Region Universities of Applied Sciences and in the Finnish National Board on Research Integrity and its working group.
| Strengths |
Enhancement areas
|
| RDI activities are based on responsible conduct of research which, in addition to the RDI services, is supported by the publications working group, project steering groups, project managers and project specialists. Cooperation with library and information services is strong. |
A system of continuous feedback regarding the state of the RDI activities, including feedback received from stakeholders. The goal is to monitor impact and report on it more systematically. |
| Metropolia is committed to the higher education institutions’ policies on open science and research by promoting an open operating culture, open learning and the openness of publications, research data and research methods. |
In accordance with measures identified in the RDIL roadmap, actors are provided support so that they may act openly on collaboration platforms and further apply the results of project work. |
| The impact of creativity in society has been promoted with perseverance. The theme has been selected as one of the spearheads of the RDI activities. |
Developing the role of coordinators for thematic areas to support cooperation between the innovation hubs and lifelong learning (RDIL). |
Metropolia is striving for innovation in areas supporting Sustainable Development
The RDI activities are managed by the director of RDI and their subordinates, the innovation directors of the five phenomenon-based innovation hubs. The Metropolia aims to enable phenomenon-based learning in innovation hubs and to link studies to RDI projects. The goal is to tackle societal phenomena through transnational cooperation. The starting point is, therefore, to grasp global challenges and trends rather than in separate skill sets. The hubs are supported by shared competence within key technologies, such as IT. The innovation directors are responsible for the operations and development of the RDI and their own innovation hubs. The RDI Services unit supports project activities.
Metropolia strategic goal is to be a bold reformer of higher education. The recent main strategic decisions and actions are evident. According to interviews, this is reflected in the new structure of four campuses and collaboration platforms with working life, such as the HyMy Village. A good example of acting boldly and quickly in an unexpected situation is the new Karamalmi campus. Management reacted to an unexpected construction problem in one old building by taking advantage of an opportunity presented by a collaboration network partner—Nokia. This led to the new Karamalmi campus. That decision and action have significantly impacted Metropolia and the society around the new campus.
Metropolia is actively seeking new RDI and artistic activities opportunities
Metropolia has a comprehensive and open view of RDI. The ‘ecosystem’ offers access to basic research through collaboration with partner universities, institutions and companies. Metropolia itself concentrates on applied RDI. In addition to its own research, innovation and development interests, Metropolia is involved in the activities of the 3AMK Alliance, which includes the two other big HEIs in the Helsinki metropolitan area. Here, Metropolia is responsible for the research theme. An established partnership model is used when forming more extended collaboration agreements.
The internet and other new technologies allow and enable employment and innovation in a fundamentally wider ‘stage’ than previously. Visual, audial and haptic elements are present in developing new products, services and buildings. For example, Metropolia’s HXRC, Helsinki Extended Reality Center, is an internationally respected technology platform with endless opportunities for art professionals. Artistic activities are actively brought nearer to and into society. The open-for-public ‘Mahdollisuuksien maisemia’ (‘Landscapes of opportunities’) event is an excellent example.
Artistic activity, however, still very much relies on highly individual skill and talent. Therefore the RDI aspect of the artistic field—also in Metropolia—relies primarily on high-quality education rather than on separate projects.
Systematic support for enhancing innovation
The ‘Metropolia spirit’ could be easily perceived in the audit interviews with staff. Metropolia’s annual planning cycle includes and involves units in systematic development. Quality management supports the RDI activities, such as project management guidelines, monitoring and development, peer reviews, steering groups, good scientific practice, ethical guidelines and action programmes. There are set targets to monitor RDI and feedback surveys, and feedback events assess it. The RDI and artistic renewal and innovation targets are present in personnel’s personal development discussions (PDDs). The bonus system is based on reaching targets, which are quarterly followed up in units’ meetings. High agility, which Metropolia is proud of, can be best utilised if it is supported on all levels by a shared, flexible and actively used quality system. Work still needs to be done with the full implementation of systematic quality tools.
During the strategic period of 2017–2022, the whole Metropolia community, including students, was invited to participate in the development of operations. One example of the participatory approach is the ‘Parru’ support service for dialogue and co-creation. This generated, for example, 50 sparring events in 2021.
Metropolia assesses the impact of its RDI activities through innovation hubs. Metropolia’s self-evaluation report also describes an ambitious RDIL roadmap, written down to activity level. Student involvement is one crucial finding of it. The focus on impact and entrepreneurship is evident, e.g. in the ‘Campus Incubator’: This cooperation with Aalto University and the city of Helsinki aims to start 100 new companies annually by the year 2030.
The audit team recommends even more active communication of the innovation strategy throughout the staff. A common understanding of future scenarios and main actions is key in leading big organisations, especially innovation-focused entities. The new strategy and the 4-campus structure will undoubtedly be helpful for this.
The library plays an essential role in promoting open science
Metropolia has systematic procedures in place to ensure good scientific practice. Metropolia is committed to the Finnish National Board in Research Integrity guidelines and to the Human Sciences Ethics Committee of the Helsinki Region Universities of Applied Sciences. Research ethics are also part of curricula in Metropolia. There is a transparent process for any suspected violations based on the responsible conduct of research (RCR). Metropolia employs two research ethics support persons and provides staff training in research ethics.
Metropolia’s focus areas are very much in touch with the real challenges of society. Both RDI and education concern various fields of science. The interviews emphasised openness and transparency well; the extensive network of universities and other external partners supports openness. Collaboration projects with companies, of course, are usually confidential, which is considered in model agreements. New innovation projects will require careful consideration regarding public accessibility. Metropolia recognises that while the open science concept prefers disclosing all results and findings to the public, most private companies will prefer confidentiality.
The library is the traditional source for open data. Nowadays, a library’s function goes beyond its collection of accessible books and publications. The information search and info network presence are organised under Metropolia’s academic services. The ability to search, understand and interpret information obtained through the internet is an essential competence for a professional. As distance learning and international cooperation increase, the significance of critical information search is growing. The library of Metropolia provides projects with reliable sources of information, guidance and information retrieval services and support for materials management and publishing.
Metropolia has also recognised the risks of ‘excessive openness ’. The current needs for information security have been recognised and acted on. In the interviews, Metropolia reported around 100,000 hack attacks per day on its information systems. Metropolia is also prepared for these cyberattacks on its quality assurance system.
